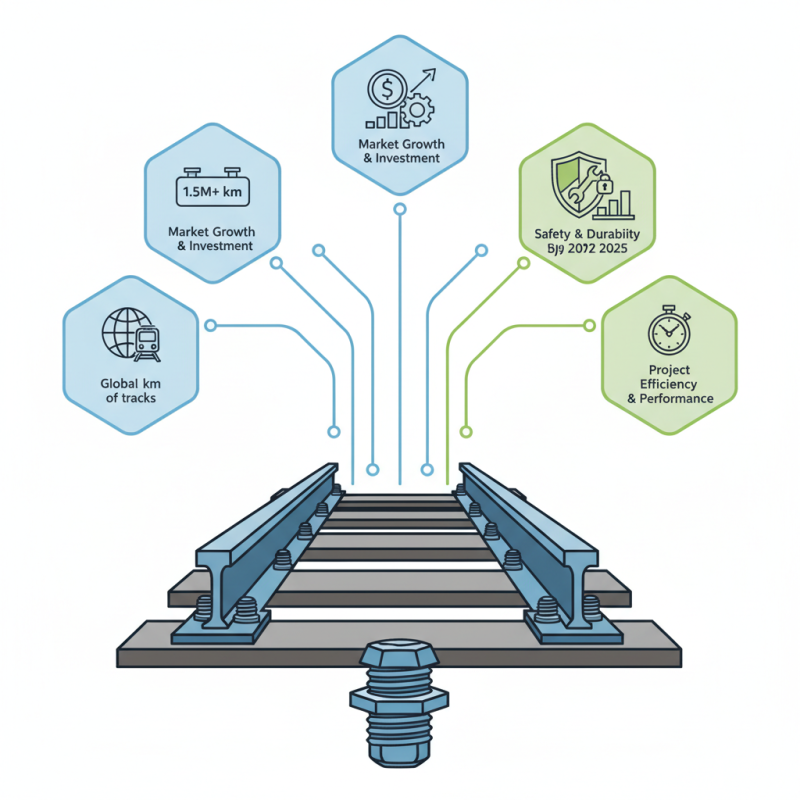
In the rail industry, the importance of selecting the appropriate hardware—particularly the railroad bolt—cannot be overstated. As rail transportation continues to expand globally, with the International Union of Railways reporting over 1.5 million kilometers of railways in operation as of 2022, the demand for reliable and durable components is paramount. Railroad bolts are critical in ensuring the structural integrity of tracks and securing various rail components under high-stress conditions, making their selection pivotal for safety and longevity.
According to industry analysts, the railroad bolt market is projected to grow significantly, driven by rising investments in rail infrastructure and modernization of existing networks. A report by MarketsandMarkets estimates that the global rail fastening systems market, which includes railroad bolts, is expected to reach USD 3.2 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the necessity for professionals in the field to carefully consider the specifications and applications of railroad bolts. Proper selection ensures not only compliance with safety standards but also enhances overall project efficiency and performance, underscoring the crucial role that railroad bolts play in the future of rail transport.
When selecting the right railroad bolt for your project, it is essential to understand the variety of types available, as each serves a distinct purpose in maintaining structural integrity and safety. Common types include track bolts, which are designed to secure rails to ties and withstand the dynamic forces exerted by passing trains. These bolts typically have specific thread patterns and require compatible nuts to ensure a secure fit. Additionally, rail anchors are vital for stabilizing track alignment and minimizing movement caused by vibrations.
Another important category is the guard rail bolt, which is used to secure guard rails, preventing them from shifting and ensuring safety at the track's edge. These bolts come in different lengths and diameters, depending on application requirements and environmental conditions. Furthermore, the choice between high-strength steel and corrosion-resistant materials will affect the durability and lifespan of the bolts, making it crucial to consider the specific demands of your project. Understanding these options helps ensure that you select the most appropriate railroad bolt, tailored to your operational needs and conditions.
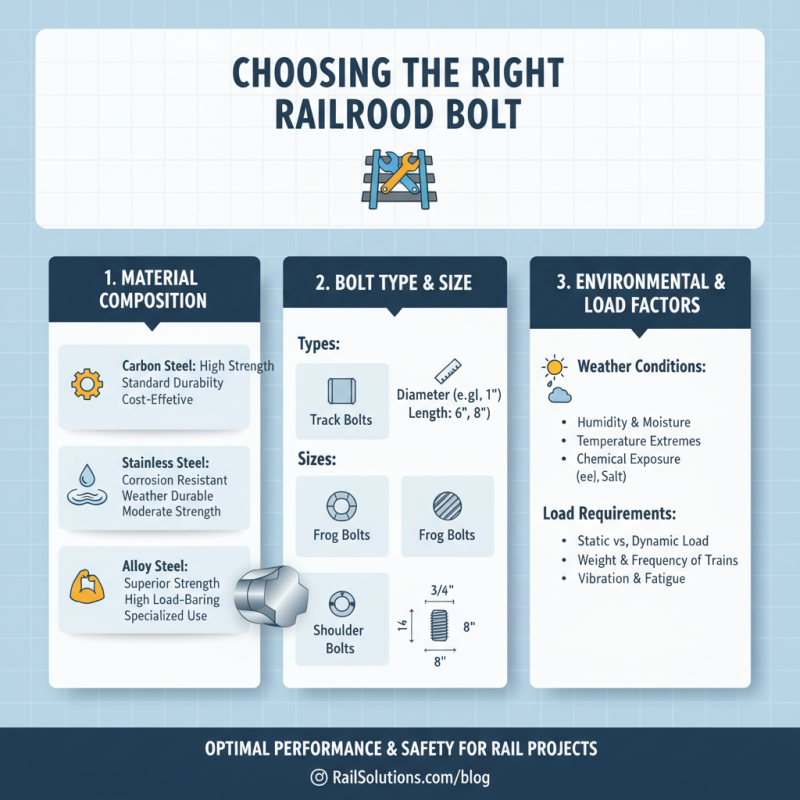
When selecting the right railroad bolt for your project, several key factors need to be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and safety. First, consider the material composition of the bolts. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, each offering varying levels of corrosion resistance and strength. The choice of material will heavily influence the bolt’s durability and suitability for different weather conditions and load-bearing requirements.
Another critical factor is the size and threading of the bolt. It's essential to match the bolt's dimensions with the specific requirements of your railroad application. This includes understanding the load specifications and environmental factors that the bolts will be subjected to. Furthermore, the type of threading, whether coarse or fine, can affect the ease of installation and the overall stability of the rail system. Ensuring that all compatibility factors are considered will lead to more effective and durable railroad infrastructure.
When selecting the right railroad bolt for your project, the material specifications play a crucial role in ensuring durability and performance. The most commonly used steel for railroad bolts is carbon steel due to its strength and versatility. Carbon steel offers excellent tensile strength and is often treated with heat to enhance its properties, making it suitable for high-stress applications. It’s essential to choose a grade of carbon steel that can withstand environmental factors such as corrosion and wear, particularly in areas with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Another vital consideration in choosing the right material is the resistance to fatigue and impact. Alloy steels can be a better option in this context, as they contain additional elements that improve hardness and toughness. These steels are particularly beneficial in applications where the bolts are subject to repeated loading or heavy impacts. Furthermore, surface treatments like galvanization or coating can provide extra protection against rust and wear, extending the lifespan of the bolts in challenging environments. By carefully considering the material specifications, you can ensure that your railroad bolts will meet the demands of your project effectively.
| Bolt Type | Material | Corrosion Resistance | Strength (ksi) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A325 | Medium Carbon Steel | Moderate | 120 | Structural Connections |
| ASTM A490 | High Strength Steel | Low | 150 | Heavy-Duty Applications |
| ASTM F3125 | Alloy Steel | High | 130 | Railroad Applications |
| Black Oxide Coated Bolt | Carbon Steel | Good | 100 | General Construction |
When it comes to selecting the right railroad bolt for your project, understanding sizing and thread types is paramount. The size of the bolt impacts not only its structural integrity but also how well it integrates with other components. Railroad bolts typically come in various diameters and lengths, and choosing the right size ensures that the bolt can bear the necessary loads without risk of failure. It is essential to consider the dimensions of the materials being joined and the specific application requirements to select a bolt that offers the right balance of strength and flexibility.
Thread types also play a critical role in bolt selection. Common thread types for railroad bolts include coarse and fine threads, and the choice between them often hinges on the application. Coarse threads provide greater resistance to stripping and are easier to install, making them suitable for applications requiring quick assembly and disassembly. On the other hand, fine-thread bolts offer better tension and adjustment capabilities, which can be advantageous in scenarios involving vibrations. Understanding these characteristics allows for a more informed choice, ensuring the selected bolts meet both safety standards and performance expectations in your project.

When installing railroad bolts, it is crucial to follow proper methods to ensure safety and durability. The first step is to prepare the surfaces where the bolts will be installed. This includes cleaning the areas to remove any debris or rust that could impede the effectiveness of the bolt. A tight fit is essential, so pre-drilling holes to accommodate the bolt size may be necessary. It is also important to use the correct torque settings to secure the bolts without over-tightening, which could damage the materials or lead to failure.
Best practices in railroad bolt installation also involve selecting the right tools. Using appropriate wrenches or impact tools can significantly enhance efficiency and accuracy. Additionally, it’s important to regularly inspect the installed bolts to monitor their condition. Over time, environmental factors and loads can stress the bolts, so maintaining a routine check-up can prevent potential accidents. Incorporating these installation methods and best practices will not only optimize the performance of railroad bolts but also contribute to the overall safety and longevity of the rail infrastructure.