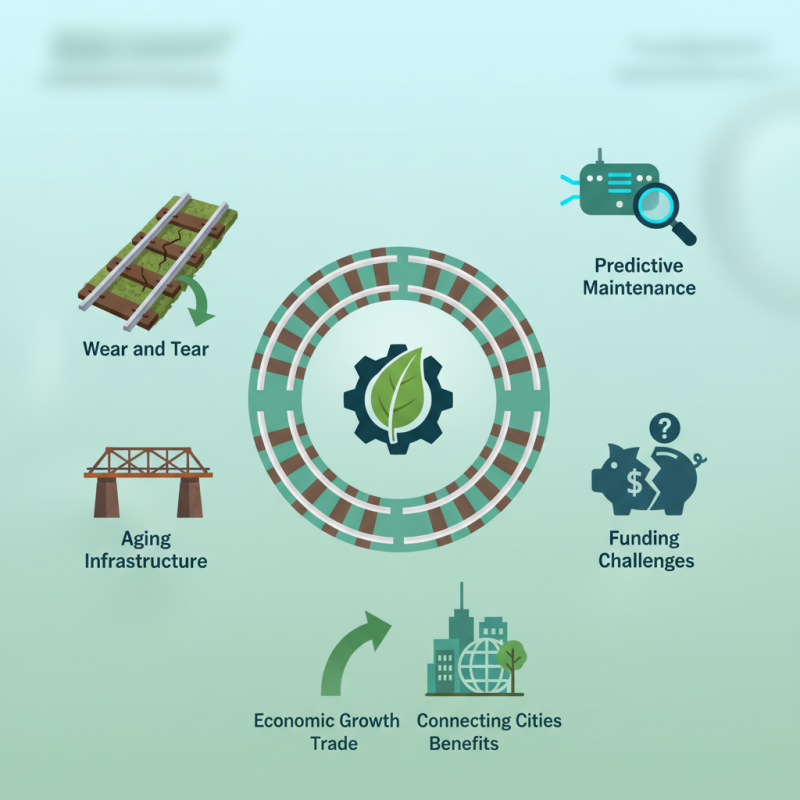
Improving railroad rail efficiency is crucial for sustainable transport. Railroad rail systems contribute significantly to the global economy. They connect cities and facilitate trade, yet they face many challenges.
One major issue is wear and tear on rails. This can lead to increased maintenance costs and accidents. Aging infrastructure is another concern. Many rail lines require upgrades to meet modern demands. We must rethink how we manage these assets.
Innovative technologies, such as predictive maintenance, could play a key role. Implementing sensors to monitor rail conditions can prevent failures. However, funding for such initiatives is often lacking. It raises the question: Are we doing enough to prioritize railroad rail efficiency? Each small improvement can lead to substantial benefits for the environment and society. We need fresh ideas and commitment to make real progress.
When assessing current railroad rail efficiency metrics, it is essential to consider multiple variables. According to the American Association of Railroads, freight trains can move one ton of freight over 480 miles on just one gallon of fuel. This impressive figure highlights the inherent efficiency of rail transport and its potential for sustainable logistics. However, a significant challenge remains: many systems still rely on outdated metrics, which fail to capture real-time performance.
Data from the International Energy Agency indicates that rail transport accounts for only 2% of the global transport energy demand. Yet, enhancing precision in efficiency metrics could lead to broader sustainability efforts. For instance, current measurements often overlook factors like infrastructure wear and freight handling delays. These neglected areas can distort true efficiency levels, warranting a reevaluation of how success is defined in rail operations.
Moreover, recent surveys indicate that nearly 30% of railroad operators report inefficiencies due to logistic misalignment. It is crucial to refine these metrics to incorporate these operational shortcomings. Without addressing these issues, the sector may miss vital opportunities to improve performance and sustainability. The focus should be on creating comprehensive assessment tools that account for both energy usage and operational flow.
This chart illustrates the efficiency metrics of different railroad systems based on various factors, such as energy consumption, load capacity, and maintenance costs.
Improving railroad rail efficiency is crucial for sustainable transport. Key factors affecting rail efficiency include track quality, train speed, and scheduling. Data from the International Energy Agency indicates that rail transport can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 75% compared to road transport. However, these benefits are only realized when rail systems operate at optimal efficiency.
Track quality significantly impacts performance. Poorly maintained tracks lead to increased wear and tear on trains. This not only raises maintenance costs but also reduces service reliability. Regular inspections and timely repairs are essential. Consider investing in advanced monitoring technology to identify track issues early.
Train speed is another critical factor. Trains running at optimal speeds can improve fuel efficiency. Yet, there can be a trade-off between speed and safety. Higher speeds may lead to more accidents if not managed correctly. Effective scheduling can enhance rail efficiency. Tight schedules may push train crews beyond safe working limits.
Tips: Monitor scheduling closely to prevent delays, which can lower efficiency. Encourage regular crew training to enhance safety and performance. Engage with engineers to assess track maintenance needs continuously. Addressing these areas will support sustainable transport goals.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Efficiency | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Track Quality | Condition of rails and ties, affects smoothness of ride. | High | Track Inspection Data |
| Train Scheduling | Optimization of timing to reduce delays. | Medium | Time Table Analysis |
| Energy Efficiency | Energy consumption rates during operations. | High | Fuel Usage Reports |
| Load Management | Proper distribution of cargo weight on trains. | Medium | Cargo Weight Distribution Reports |
| Technological Upgrades | Implementation of modern signaling and communication systems. | Very High | Technology Assessment Reports |
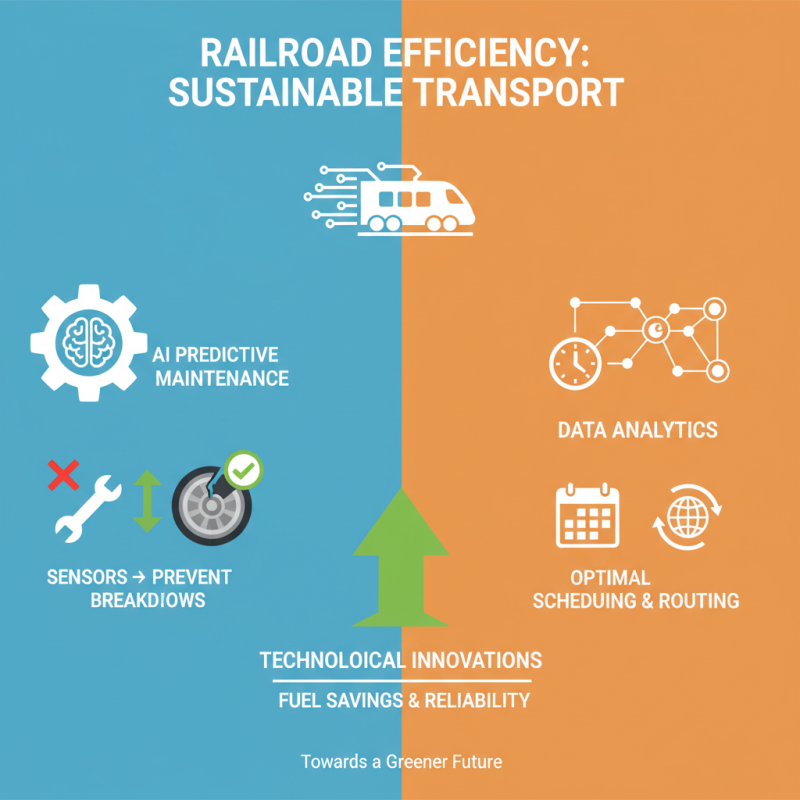
Railroad efficiency is crucial for a sustainable transport future. Technological innovations play a key role in achieving this goal. One major advancement is the use of AI for predictive maintenance. Sensors on trains monitor wear and tear. This helps prevent breakdowns and delays. Data analytics provides insights into optimal scheduling and routing.
Moreover, lighter materials are being used for rail cars. This reduces energy consumption during transit. Additionally, electrification of rail lines is gaining momentum. Electric trains produce fewer emissions than traditional diesel models. However, the initial infrastructure costs can be high, leading to criticism.
Automation is another exciting area. Automated systems can enhance safety and improve operational speeds. Yet, it is vital to address potential job losses. Workers must be retrained for new roles. Balancing innovation and workforce needs is an ongoing challenge. The path to improved railroad efficiency is paved with both opportunities and obstacles.
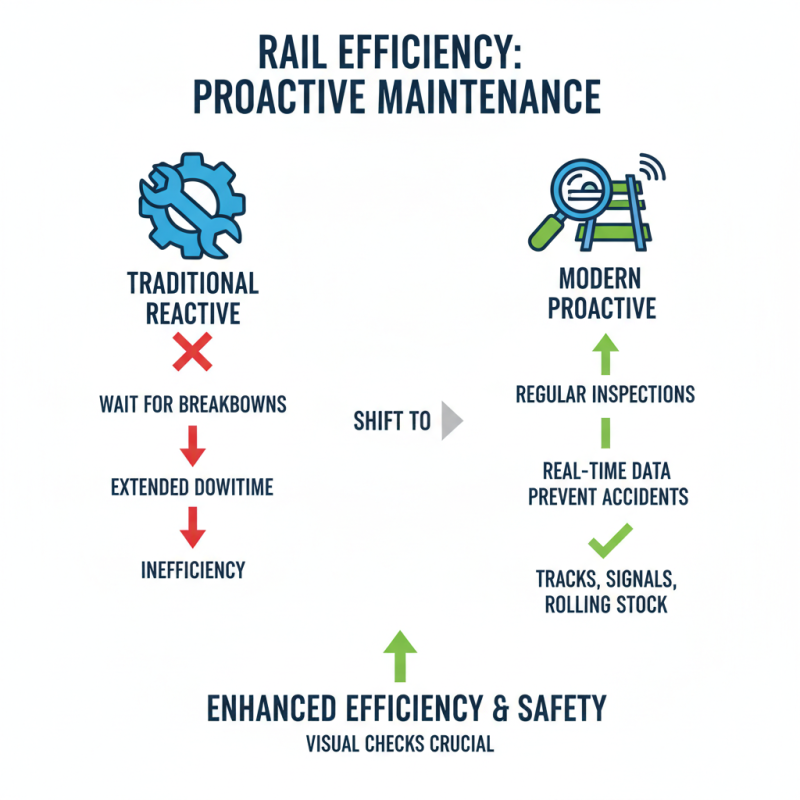
Rail maintenance and operations play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency. Regular inspections are vital. Checking tracks, signals, and rolling stock ensures everything runs smoothly. A simple visual check of rail integrity can prevent accidents. However, many operations still rely heavily on reactive maintenance. This approach often leads to extended downtimes and inefficiencies. A more proactive strategy, relying on real-time data, could make a significant difference.
Efforts to institutionalize best practices can yield benefits. Developing training programs for staff focusing on sustainability is essential. Employees should understand the environmental impact of their work. In addition, integrating technology, such as predictive analytics, can illuminate potential failures before they escalate. Yet, many railway organizations struggle with the adoption of new systems. Resistance to change is common. It might slow down progress towards a more sustainable future.
Efficient operations often require collaboration among stakeholders. Engaging local communities in discussions about rail improvements can foster a sense of shared responsibility. This approach can build trust and support for sustainability efforts. However, coordination between different parties can be complex. Miscommunication can lead to fragmented initiatives. A more unified direction could enhance overall efficiency and sustainability in railways.
Sustainable rail transport is crucial for reducing carbon emissions. According to the International Energy Agency, trains are four times more efficient than trucks in moving freight. Yet, rail systems face inefficiencies daily. Infrastructure upgrades and better management are necessary to shift towards sustainability.
Policy recommendations can drive improvements. Investing in electrification is one of them. Electrified rail lines produce fewer emissions. They can reduce operating costs significantly. According to a recent report, electrified trains can lead to a 30% decrease in energy consumption. This is a compelling reason for governments to prioritize such initiatives.
Tip: Consider regional needs. Different areas may require different solutions. A one-size-fits-all approach often leads to inefficiencies. Another important aspect is technology. Sensor systems can optimize train schedules, reducing delays. However, not all regions are prepared for this tech upgrade. Continuous training for workforce adaptation is also critical.