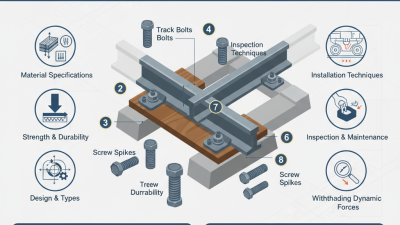
Railroad bolts are critical components in the infrastructure of railway systems, playing a pivotal role in ensuring track stability and safety. These specialized fasteners secure track components, such as rails and ties, maintaining the alignment and integrity of the entire railway structure. As trains traverse these tracks at varying speeds and weights, the reliability of railroad bolts becomes increasingly significant. A failure in these bolts can lead to track misalignment, increasing the risk of derailments and accidents.
Furthermore, the material composition and design of railroad bolts are tailored to withstand the extreme conditions that railways often confront, including fluctuating temperatures, heavy loads, and constant vibrations. The importance of these bolts can be understood not just in terms of their mechanical function, but also in their contribution to the overall safety culture in rail transport. As transportation networks evolve, the demand for robust and reliable components, like railroad bolts, grows, highlighting the necessity of ongoing maintenance and innovation in rail fastening technologies. Understanding the essential role of railroad bolts provides insight into the foundational elements that keep railway systems operational and safe for passengers and goods alike.
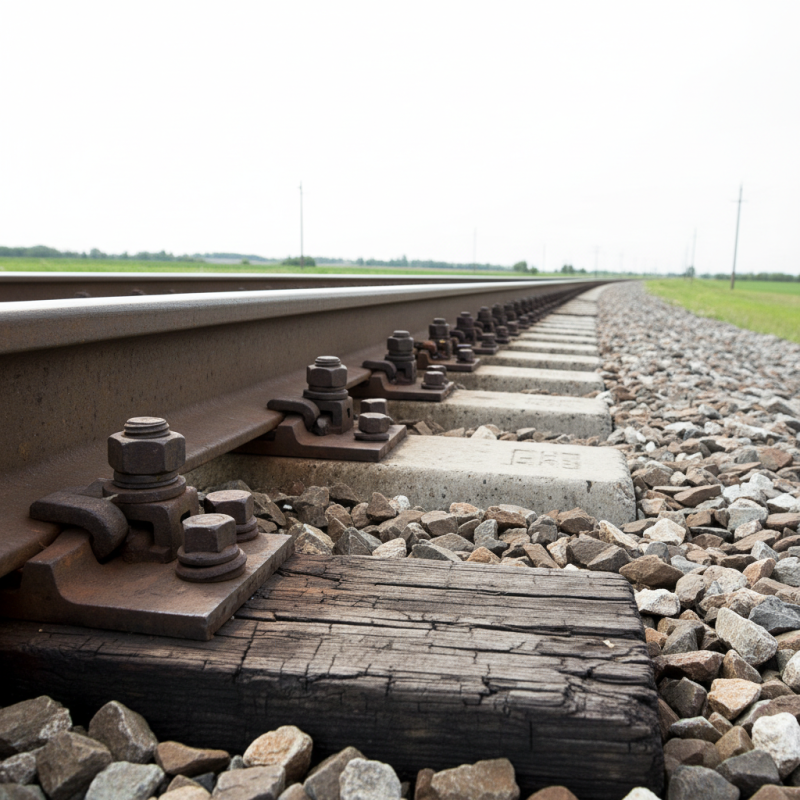

Railroad bolts play a critical role in maintaining the stability of railway tracks, ensuring that they can withstand the stresses of heavy train loads and adverse weather conditions. These bolts serve as fasteners that hold the rails securely to the ties, preventing movement that could lead to dangerous derailments. The proper installation and maintenance of railroad bolts are essential in preserving the integrity of the track structure. Variations in temperature and deformation due to repeated stress can weaken the connection, which is why regular inspections and timely replacements are necessary to maintain safety standards.
Moreover, the design of railroad bolts is specifically engineered to provide a robust connection. They are often made from high-strength materials that can endure significant forces, thus contributing to the overall stability of the rail infrastructure. With the ability to absorb vibration and reduce lateral movement, these bolts ensure that the track remains aligned and functional. Their effectiveness in maintaining a secure bond between rails and ties directly translates to increased safety for both freight and passenger trains, making them indispensable components of railway systems.
Railroad bolts play a critical role in ensuring the stability and safety of railway tracks. Depending on the track class, different types of bolts are used to meet specific requirements. For instance, heavier gauge bolts are typically employed in Class 1 and Class 2 tracks, which support freight trains traveling at higher speeds and weights. According to the Federal Railroad Administration, the appropriate fastening system, including bolts, can significantly improve track integrity and reduce derailment risks.
On the other hand, lighter-duty bolts may be sufficient for Class 3 and Class 4 tracks, which accommodate lower-speed passenger trains. These bolts, while less robust, still need to provide adequate resistance to the forces exerted during operation. Recent studies suggest that using the correct type of bolt is vital; improperly matched bolts can lead to track misalignment, resulting in reduced safety margins. A report by the Transportation Research Board indicates that maintaining the right specifications for track hardware can lower maintenance costs over time by increasing the lifespan of both bolts and ties. Ultimately, understanding the different types of railroad bolts and their application according to track classes is essential for maintaining the overall safety of railway systems.

The integrity of railroad bolts is crucial for maintaining track stability, particularly in regions subjected to extreme weather conditions. Temperature fluctuations can cause metal expansion and contraction, leading to loosening or even breaking of bolts over time. Rain, snow, and ice can accelerate rust and corrosion, compromising the bolts' strength. A failing bolt can lead to misalignment of the tracks, increasing the risk of derailments and accidents. Therefore, regular inspections and timely replacements are necessary to counteract the adverse effects of such environmental factors.
Additionally, the wear and tear from the relentless movement of trains exert significant stress on railroad bolts. Vibration and heavy loads can cause bolts to gradually become loose, making them susceptible to further damage from weather-related factors. Inconsistent maintenance can exacerbate these issues, resulting in a higher likelihood of bolt failure. It is essential for railroad operators to implement proactive measures, including routine checks and climate-resilient materials, to enhance bolt durability and ensure the safety of train operations.
Railroad bolts play a crucial role in maintaining track stability and safety, but their effectiveness relies heavily on regular maintenance practices. Railroad workers must routinely inspect and tighten these bolts to ensure they securely fasten tracks to the underlying ties. Loose or damaged bolts can lead to misalignment of the tracks, increasing the risk of derailments. Regular monitoring not only identifies potential issues early but also helps maintain the integrity of the rail system as a whole.
In addition to periodic inspections, proper replacement of worn or corroded bolts is vital. Utilizing high-quality materials and modern fasteners can enhance the longevity of railroad bolts. Furthermore, adopting advanced technologies, such as ultrasonic testing, allows for the detection of hidden flaws that could compromise safety. Comprehensive maintenance practices, including lubrication and protective coatings, also help mitigate wear and environmental damage. By prioritizing these practices, railways can improve safety and reliability, ensuring a stable infrastructure for efficient transportation.
Improperly installed or maintained railroad bolts can lead to catastrophic consequences that compromise both track stability and safety.
When bolts are not fastened correctly, they can become loose, resulting in misaligned rails. This misalignment can cause trains to derail, leading to potential injuries, casualties, and significant damage to both infrastructure and rolling stock.
A simple oversight in bolt installation can therefore have far-reaching implications, endangering both passengers and freight.
Furthermore, lack of regular maintenance can exacerbate these issues. Over time, rust and environmental factors can weaken bolts, making them susceptible to failure.
When bolts corrode or break, entire sections of track can become unstable, significantly increasing the risk of derailments.
Regular inspections and timely replacements of bolts are crucial in preventing such failures and ensuring the safe operation of trains.
This emphasizes the importance of thorough maintenance protocols and the critical role that railroad bolts play in the overall safety of rail transport systems.